The Quaker Parrot: A Comprehensive Guide to the Monk Parakeet
The Quaker Parrot, also known as the Monk Parakeet (scientifically as Myiopsitta monachus), is a remarkable bird known for its intelligence, vibrant personality, and distinctive social structure.
Native to South America, these parrots have found homes in many parts of the world, captivating bird enthusiasts and researchers alike. This blog delves into the world of Quaker Parrots, exploring their physical characteristics, behavior, habitat, and the unique challenges they face.
Introduction to the Quaker Parrot

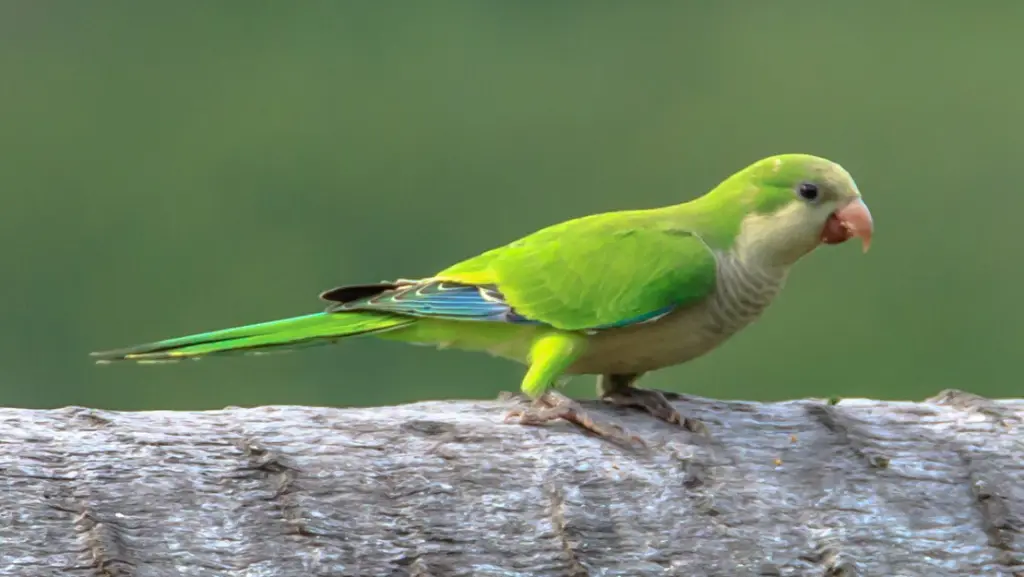
Quaker parrot (Monk parakeet)
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Size | Small parrot species, weighing up to 140 grams |
| Color | Mossy green back, grey front, blue flight feathers |
| Long tails and a distinctive skin-colored beak | |
| Behavior | Talkative and social; can live for decades |
Quaker Parrots are small to medium-sized birds with a distinctive appearance and a remarkable ability to adapt to various environments. Their charming personality and ability to mimic human speech have made them popular pets. However, their establishment in the wild outside their native range has led to both fascination and concern due to their impact on local ecosystems.
Physical Characteristics
Quaker Parrots are easily recognizable by their green plumage and greyish breast, which gives them their “quaker” name, as it resembles an old-fashioned Quaker costume. They typically measure about 29 cm (11 inches) in length and weigh between 90 to 120 grams (3.2 to 4.2 ounces). Their wings are long and pointed, providing excellent maneuverability in flight. The tail is also long and tapered, aiding in their agile movements.
One of the most striking features of Quaker Parrots is their expressive face, with bright eyes and a robust beak. Their beak is designed for cracking seeds and nuts, which form a significant part of their diet. The beak’s strength is complemented by their dexterous feet, which they use to hold food while eating.
Habitat and Distribution
Originally, Quaker Parrots are native to the temperate and subtropical regions of South America, particularly in countries like Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay. They inhabit woodlands, savannas, and urban areas, demonstrating a remarkable adaptability to different environments.
In recent decades, Quaker Parrots have established feral populations in various parts of the world, including North America, Europe, and Asia. These populations often result from escaped or released pet birds. In the United States, for instance, significant feral populations exist in states such as Florida, Texas, and New York, where the climate is conducive to their survival.
Behavior and Social Structure
Quaker Parrots are highly social birds, known for their complex social structures and communal nesting habits. These traits have contributed to their success in both their native and introduced ranges.
Communal Nesting
One of the most fascinating aspects of Quaker Parrot behavior is their communal nesting. Unlike most parrots, which nest in tree cavities or burrows, Quaker Parrots build large, elaborate nests out of twigs and branches. These nests can house multiple pairs, each with its own chamber, creating a condominium-like structure. This communal living provides several advantages, including enhanced protection from predators and shared responsibilities in raising young.
Vocalizations and Communication
Quaker Parrots are highly vocal and capable of mimicking human speech and other sounds. Their vocalizations are not just random noises but serve specific purposes such as establishing territory, signaling alarm, and maintaining social bonds. In captivity, their ability to learn and reproduce a wide range of sounds makes them popular pets, although their loud calls can sometimes be a challenge for owners.
Intelligence and Problem-Solving
These parrots are renowned for their intelligence and problem-solving abilities. They are quick learners, capable of understanding and performing complex tasks. In captivity, they can be trained to do tricks, use interactive toys, and even solve puzzles. This high level of intelligence requires mental stimulation to prevent boredom and behavioral issues.
Quaker Parrots as Pets
The Quaker Parrot’s engaging personality and ability to bond with humans make them a popular choice for pet owners. However, owning a Quaker Parrot comes with specific responsibilities and challenges that potential owners should be aware of.
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet is crucial for the health and well-being of Quaker Parrots. In the wild, their diet consists mainly of seeds, fruits, vegetables, and nuts. In captivity, a similar diet should be provided, supplemented with high-quality pellet food to ensure they receive all necessary nutrients.
Fresh fruits and vegetables should be offered daily, including leafy greens, carrots, apples, and berries. Seeds and nuts should be given in moderation due to their high-fat content. It is also essential to provide clean, fresh water at all times.
Housing and Environment
Quaker Parrots are active and playful birds that require ample space to move and explore. A spacious cage with plenty of room for flying and climbing is essential. The cage should be equipped with perches, toys, and climbing structures to keep the bird mentally and physically stimulated.
Outside the cage, Quaker Parrots need regular opportunities to exercise and interact with their human companions. Supervised out-of-cage time is crucial for their well-being and helps to prevent behavioral issues.
Social Interaction and Training
Quaker Parrots are social creatures that thrive on interaction with their human family. Regular socialization and bonding activities are essential to keep them happy and healthy. Training sessions can be an excellent way to provide mental stimulation and strengthen the bond between the bird and its owner.
Positive reinforcement techniques, such as treats and praise, are effective in training Quaker Parrots. They can learn a variety of commands, tricks, and even how to talk. Consistency and patience are key to successful training.
Health and Veterinary Care
Regular veterinary check-ups are vital for monitoring the health of Quaker Parrots. Like all birds, they are susceptible to various health issues, including respiratory infections, feather plucking, and nutritional deficiencies. A qualified avian veterinarian can provide guidance on preventive care and treatment if health issues arise.
Challenges and Controversies
While Quaker Parrots are beloved by many, their presence in non-native areas has sparked controversy due to their impact on local ecosystems and infrastructure.
Invasive Species Concerns

In some regions, feral populations of Quaker Parrots are considered invasive. Their communal nesting habits can cause damage to trees and utility structures, leading to costly repairs and maintenance. Additionally, their competition with native bird species for food and nesting sites can negatively impact local biodiversity.
Efforts to manage and control feral populations vary by region. Some areas implement removal programs, while others focus on public education and habitat management to mitigate the impact of these birds.
Legal Restrictions
Due to their potential as an invasive species, Quaker Parrots are subject to legal restrictions in some areas. In the United States, for example, ownership and breeding of Quaker Parrots are regulated in certain states. Potential owners should familiarize themselves with local laws and regulations before acquiring a Quaker Parrot.
Conservation Status and Efforts
In their native range, Quaker Parrots are not currently considered endangered. However, habitat destruction and changes in land use can pose threats to their populations. Conservation efforts focus on preserving their natural habitats and ensuring sustainable coexistence with human activities.
Habitat Preservation
Protecting the natural habitats of Quaker Parrots in South America is crucial for their long-term survival. Conservation organizations work to safeguard forests and other critical habitats from deforestation and degradation. These efforts benefit not only Quaker Parrots but also a wide range of other species that share their ecosystem.
Research and Monitoring
Ongoing research and monitoring are essential for understanding the population dynamics and ecological needs of Quaker Parrots. Field studies provide valuable data on their behavior, breeding, and migration patterns, informing conservation strategies and management plans.
Community Engagement
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is vital for the success of these initiatives. By involving people in habitat restoration projects and educational programs, conservationists can foster a sense of stewardship and encourage sustainable practices that benefit both wildlife and human communities.
Conclusion
Quaker Parrots are remarkable birds that captivate with their intelligence, social behavior, and adaptability. Whether in their native South American habitats or as introduced populations around the world, these birds leave a lasting impression on those who encounter them.
As pets, they bring joy and companionship to countless households, provided their needs for social interaction, mental stimulation, and proper care are met. In the wild, their unique nesting habits and social structures offer fascinating insights into avian behavior and ecology.
However, the challenges posed by their introduction to non-native areas highlight the importance of responsible ownership and effective management strategies. By balancing the needs of Quaker Parrots with the preservation of local ecosystems, we can ensure that these charming birds continue to thrive for generations to come.
The Social Dynamics of Quaker Parrots
The social dynamics of Quaker Parrots are complex and integral to their behavior both in the wild and in captivity. Understanding these dynamics can provide deeper insights into their interactions and enhance the care provided to them as pets.
Hierarchical Structures
In their natural habitat, Quaker Parrots exhibit hierarchical social structures within their colonies. Dominance hierarchies influence access to resources such as food and nesting sites. These hierarchies are maintained through various social interactions, including vocalizations, displays, and sometimes physical confrontations.
Bonding and Relationships
Bonding is a significant aspect of Quaker Parrot behavior. These birds form strong pair bonds that often last for life. Mated pairs engage in mutual preening, feeding, and close physical contact, strengthening their bond and ensuring cooperative breeding success. In captivity, a Quaker Parrot can form a strong bond with its human caregiver, often showing preference and affection towards them.
Cooperative Breeding
Quaker Parrots practice cooperative breeding, where multiple individuals help care for the young. This behavior is relatively rare among birds and provides several advantages, such as increased survival rates for chicks and reduced predation risk. In captivity, this cooperative nature can manifest as strong bonds within a flock, with multiple birds participating in the care and protection of the group’s offspring
.
Environmental Adaptability
One of the key factors contributing to the success of Quaker Parrots in various environments is their remarkable adaptability. This adaptability is evident in their diet, nesting habits, and ability to thrive in urban settings.
Diet Flexibility
Quaker Parrots are opportunistic feeders with a diverse diet. In addition to seeds and nuts, they consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, and occasionally small invertebrates. This dietary flexibility allows them to exploit different food sources depending on availability, contributing to their success in both wild and urban environments.
Urban Living
In urban areas, Quaker Parrots have adapted to living alongside humans. They often nest on man-made structures such as utility poles, buildings, and even traffic lights. These urban nests can sometimes cause conflicts with human activities, but they also demonstrate the parrot’s incredible ability to adjust to different living conditions.
Temperature Tolerance
Quaker Parrots can tolerate a range of temperatures, from the subtropical climates of their native South America to the colder winters in some of their introduced ranges. Their communal nesting behavior helps them maintain warmth and protect against harsh weather conditions, further enhancing their survival in various climates.
The Quaker Parrot’s Role in Ecosystems
In their native range, Quaker Parrots play a crucial role in their ecosystems. Their activities as seed dispersers and their interactions with other species contribute to the health and diversity of their habitats.
Seed Dispersal
As frugivores, Quaker Parrots consume a variety of fruits and disperse the seeds through their droppings. This seed dispersal is vital for the regeneration of forests and the maintenance of plant diversity. By spreading seeds across different areas, they help ensure the growth of new plants and the continuation of forest ecosystems.
Interactions with Other Species
Quaker Parrots interact with a range of other species, both as competitors and as part of a broader ecological network. Their nests provide habitat for other organisms, including insects and small mammals, creating a micro-ecosystem within the larger environment. These interactions highlight the interconnectedness of species and the importance of maintaining balanced ecosystems.
Ethical Considerations of Quaker Parrot Ownership
Owning a Quaker Parrot comes with ethical responsibilities that prospective and current owners should carefully consider. Ensuring the well-being of these intelligent and social birds requires a commitment to their physical and emotional needs.
Ethical Breeding Practices
Prospective owners should seek out reputable breeders who practice ethical breeding. This includes providing proper care for breeding pairs, ensuring genetic diversity, and avoiding inbreeding. Ethical breeders prioritize the health and well-being of their birds, contributing to the overall welfare of the species in captivity.
Avoiding Illegal Trade
The illegal trade of Quaker Parrots poses significant threats to wild populations and contributes to unethical practices. Potential owners should avoid purchasing birds from dubious sources and instead support legal and responsible avenues for acquiring pets. By doing so, they help combat wildlife trafficking and promote conservation efforts.
Commitment to Long-Term Care
Quaker Parrots have long lifespans, often living 20 to 30 years or more in captivity. Potential owners must be prepared for a long-term commitment, ensuring that they can provide consistent care, social interaction, and mental stimulation throughout the bird’s life. Understanding the time, effort, and resources required to care for a Quaker Parrot is essential for responsible ownership.
Conclusion
Quaker Parrots, with their vibrant personalities, social complexity, and adaptability, are fascinating birds that offer much to both the natural world and those who choose to keep them as pets. Their presence in various environments highlights their remarkable adaptability and the need for responsible management to balance their benefits and challenges.
As pets, Quaker Parrots bring joy and companionship, provided their needs for social interaction, mental stimulation, and proper care are met. In the wild, their unique nesting habits and social structures offer valuable insights into avian behavior and ecology.
The challenges posed by their introduction to non-native areas underscore the importance of responsible ownership and effective management strategies. By balancing the needs of Quaker Parrots with the preservation of local ecosystems, we can ensure that these charming birds continue to thrive for generations to come. Through conservation efforts, research, and community engagement, we can protect the natural habitats of Quaker Parrots and promote sustainable coexistence with these remarkable birds.